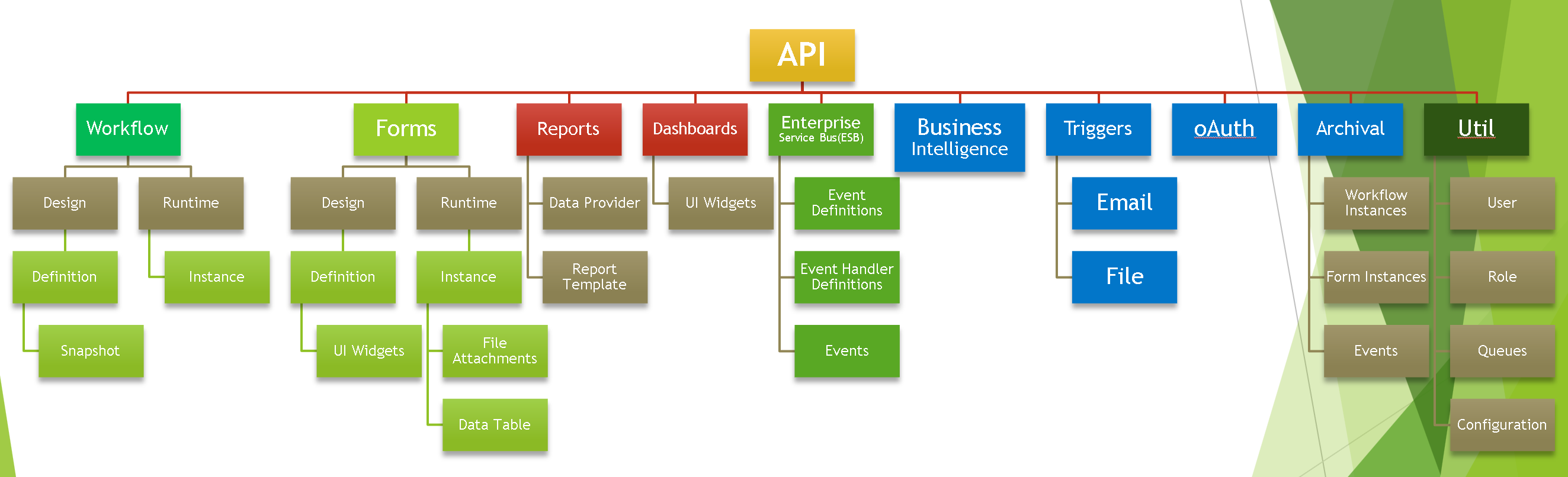
The FlowWright high level API is the main API for all FlowWright components, user interface, business logic, engines and gives all access to functionality and objects within FlowWright. The API is divided into parent/child objects as described below:
- deDesign - contains functionality for all design time objects, is able to create/get deWorkflowDefinition objects
- deRuntime - contains functionality for all runtime objects, is able to get access to deWorkflowInstance objects
- deFormDesign - access to deFormDefinitons
- deFormRuntime - access to deFormInstances
- deBusinessIntelligence - access to BI functions
The below diagram illustrates the objects involved within the high level API:

API is pretty large yet very simple to use. The above diagram defines objects and their hierarchy. Most object use 2 standard constructors. FlowWright constructors require very minimum amount of information:
- connection string to the FlowWright database
- external user name
Just with these 2 pieces of information any object within FlowWright can be created. For example, in order to create the deDesign object, the constructor looks as follows:
deDesign oDesign = new deDesign("db connection string", "external user name");
Once the oDesign object is created, all design methods and functionality are available. Objects such as deWorkflowDefintion are set to internal ONLY. What that means is, they are not creatable, objects by outside applications. These objects have to retrieved using the parent objects of the API, so to get a deWorkflowDefinition object, you would perform the following calls:
deDesign oDesign = new deDesign("db connection string", "external user name");
deWorkflowDefintion oDef = oDesign.getDefinition("defintion id");
It's the same for deWorkflowInstances object, the deRuntime object must be used to retrieve the deWorkflowInstance object.
What the reason for this? Well, when you ask for an object such as the deWorkflowDefinition from the deDesign object, we perform all the error checking, validation. If the workflow definition exists, then its returned otherwise NULL is returned by the API.
As the API is separated into many classes, they are organized by design and runtime mainly. Others are single level classes that provide specific functionality through the API. There are many API code examples within the FlowWright knowledgebase, but also within the Developers guide and getting started with the API guide.